InsightsUltrasonic Cleaning of Electronic Components
Cleaning assemblies using ultrasonic systems: What you need to know about ultrasonic cleaning for the electronics industry
cleaning processesEffective Assembly Cleaning Through Ultrasound
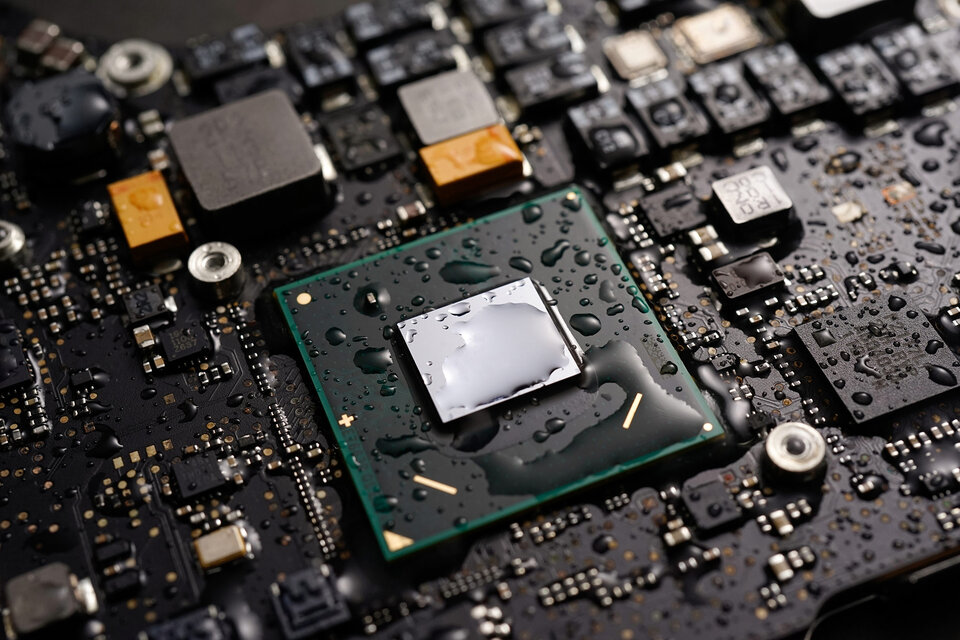
Ultrasonic cleaning is an important process in assembly cleaning and is used as part of a broader cleaning process that also includes other steps such as rinsing and drying. The goal is to remove contamination on the surface of assemblies and components as well as under the components using ultrasound.
Ultrasonic transducers in a cleaning system generate high-frequency sound (pressure) waves that create cavitation bubbles throughout the cleaning bath. These bubbles are only a few micrometers in size and change depending on the periodic pressure variation. They grow, shrink, implode even near the surface of the part to be cleaned, and generate pressure jets during implosion, which detach particles, flux residues, oils, and other contaminants from the surface of the assembly.
application Which Components are Suitable for Ultrasonic Cleaning?
Ultrasonic cleaning is suitable for a variety of components and assemblies, especially if they possess hard-to-reach areas. For electronic assemblies, these can be printed circuit boards, connectors, relays, switches, sensors, etc. Even delicate surfaces can often be cleaned with modern ultrasonic systems..
In general, ultrasonic cleaning is suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, and rubber. However, it is important to note that not all materials are suitable for ultrasonic cleaning. Specific cleaning requirements and material compatibility should always be considered before the process is applied.

why ultrasonic cleaning? Ultrasonic Cleaning Offers Several Advantages:
-
Efficiency: Ultrasonic cleaning can reach hard-to-access areas, such as under components with low standoff heights.
-
Thoroughness: The microscopic cavitation bubbles can remove even the finest contaminants.
-
Time and Cost Savings: Since ultrasonic cleaning enables efficient and thorough cleaning, it can reduce time and labor costs.
ultrasonic cleaning processWhat Should be Considered When Installing an Ultrasonic Process?
Ultrasonic cleaning generally is an efficient method in assembly cleaning. However, certain framework conditions must be considered, such as:
-
Definition of your cleaning requirements
What type of contamination is present, what materials are used, what does this mean for material compatibility? -
Selection of a suitable system based on requirements
The planned throughput of assemblies plays a role in the size of the system. The power and other equipment features must also be considered. -
Setup of parameters
Ultrasonic systems have predefined frequencies for cleaning. It must be evaluated whether these frequencies are compatible with the components on your assembly with appropriate trials.
Our experts can help you determine whether your process around your assemblies to be cleaned is suitable for an ultrasonic process and what additional considerations are required. We support you with our expertise and offer you options.
From practiceUltrasonic Cleaning among Compounds
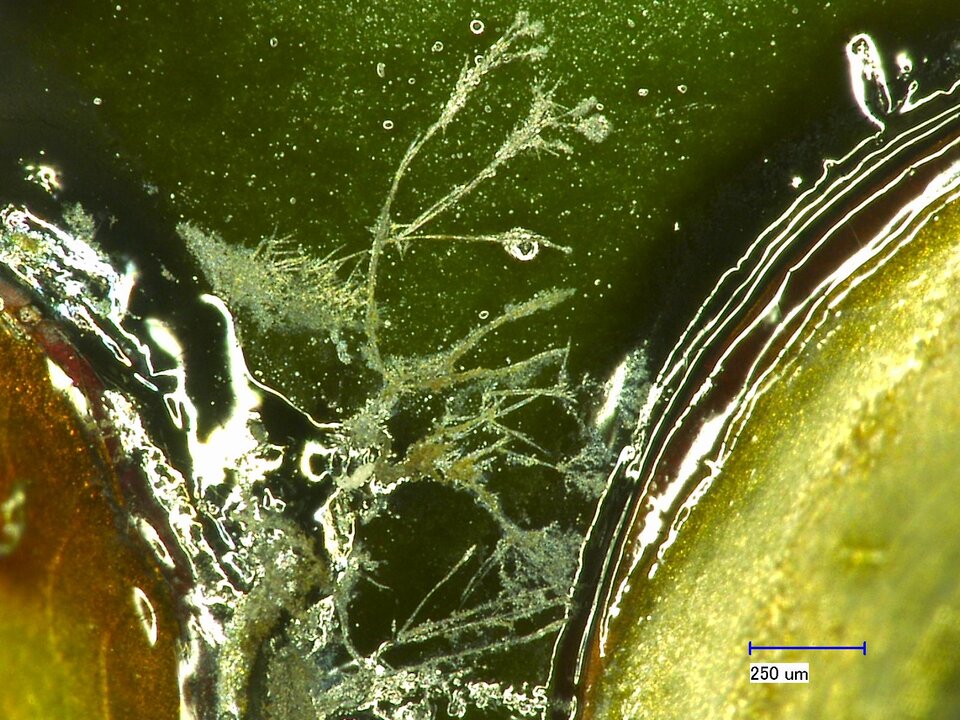
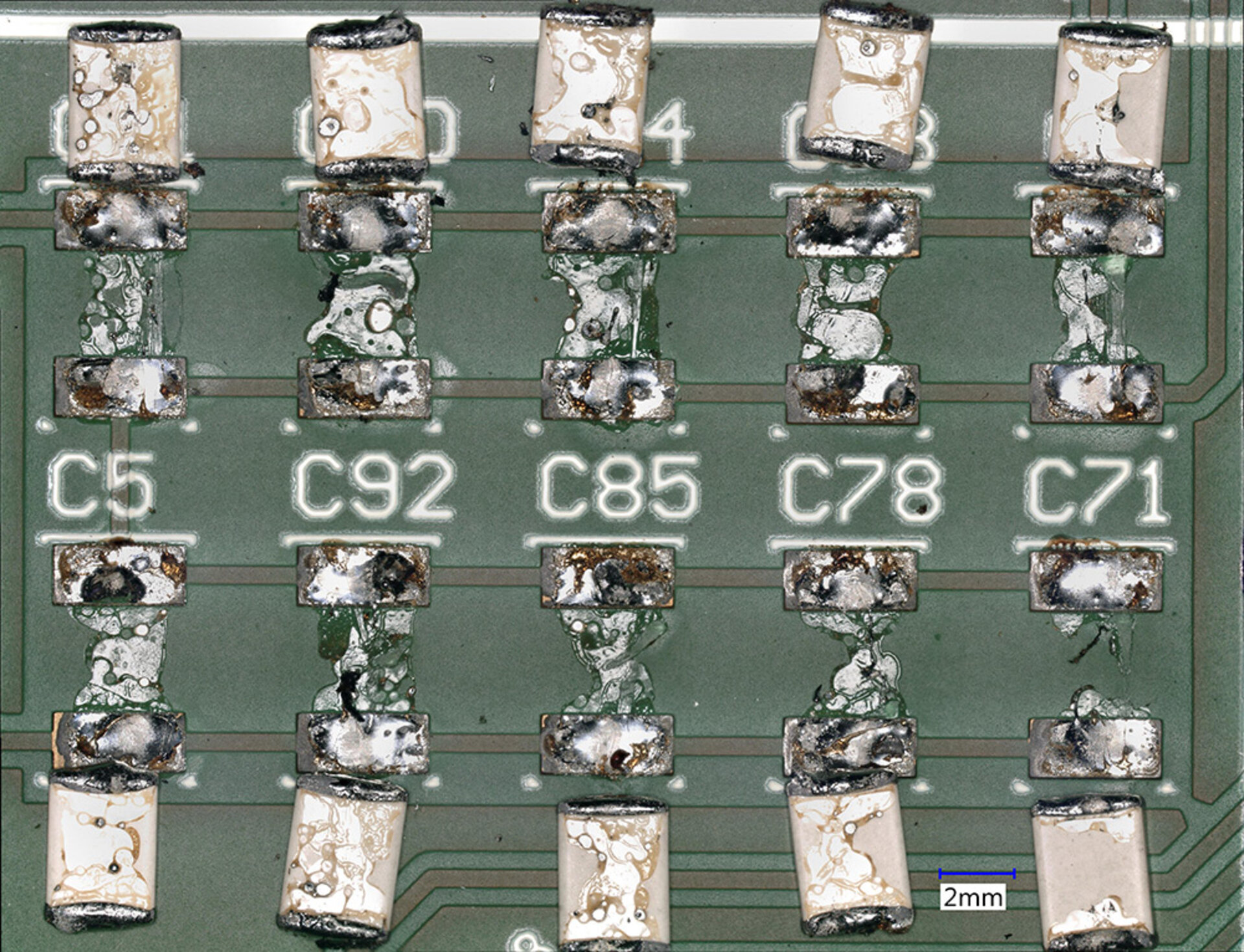
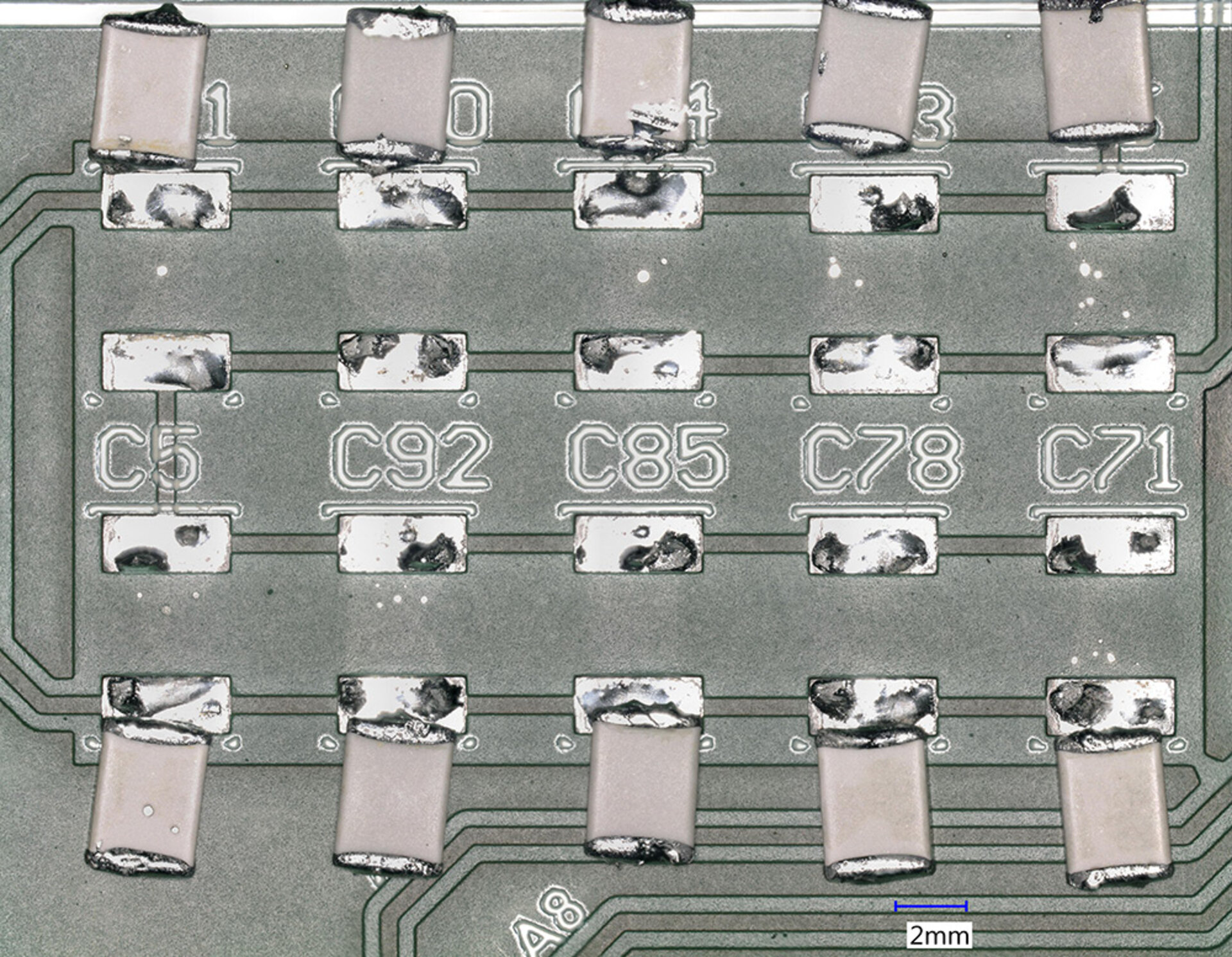
When components are soldered onto printed circuit boards, flux residues always arise. These can manifest visibly around the solder pads or be hidden beneath the components. The left image shows soldered-on and subsequently desoldered chip capacitors with flux residues beneath the stand-offs. If the residues are not removed, this can lead, for example, to dangerous short circuits and thus to the failure of the assembly. The right image shows these areas after ultrasonic cleaning. The flux residues have also been reliably removed from beneath the capacitors
We support youDo You Want to Introduce an Ultrasonic Process?
Our experienced process engineers are happy to help you.

Whitepaper-CollectionAdvanced and Gentle Ultrasonic Cleaning
Despite myths about ultrasonic damage to circuit boards, innovations by machine suppliers and the IPC ensure safe cleaning. This Whitepaper explains how modern ultrasonic cleaning works, highlighting the importance of correct frequency, setup, and standardized testing for gentle, effective cleaning.