InsightsIon Chromatography or Rose Test: Measure the Ionic Contamination on the Surface of PCBs
Accurate measurement of ionic contaminants is crucial to ensure the reliability of your assemblies.
analytical servicesROSE Test or Ion Chromatography: Accurate Measurement of Ionic Contamination
The presence of ionic contamination on the surfaces of electronic assemblies, combined with moisture, can lead to failures and damages such as corrosion, electrochemical migration, or short circuits. To ensure the reliability and longevity of assemblies, regular testing for ionic contamination is often essential.
To identify and assess these potential ionic contaminations precisely, we offer our customers two proven analytical services: the ROSE Test and ion chromatography.
simple methodROSE Test: Rapid Overview
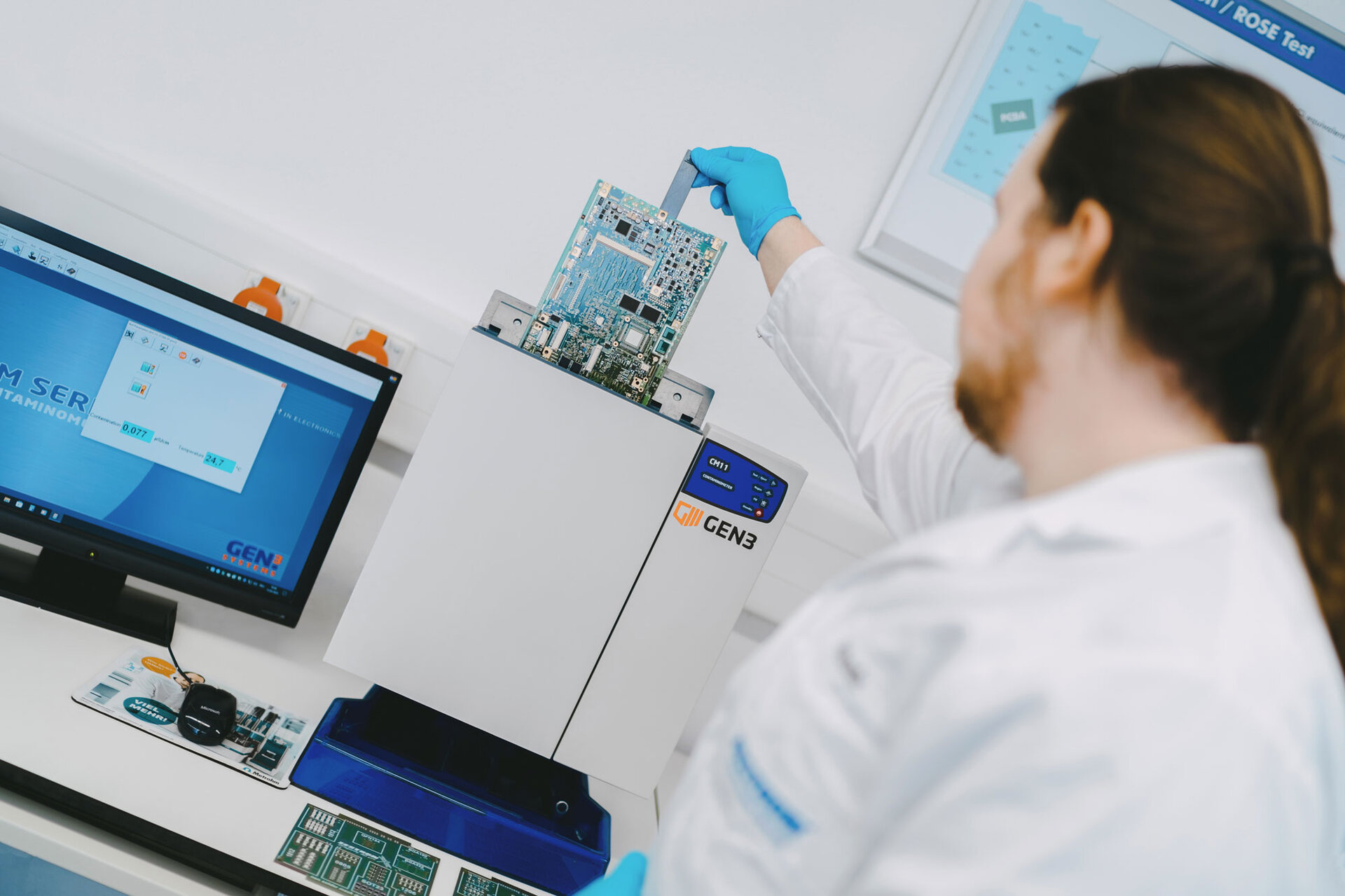
The ROSE test (Resistivity of Solvent Extract) is an established and simple method for determining ionic contamination on circuit boards and assemblies. The measurement is based on the change in conductivity and provides a summation value that relates the total ionic contamination to sodium chloride.
The ROSE Test provides a quick and comprehensive overview of the ionic cleanliness of circuit boards and assemblies. However, it does not provide a detailed representation of the contamination. This is where the high-resolution analytical method of ion chromatography comes into play.
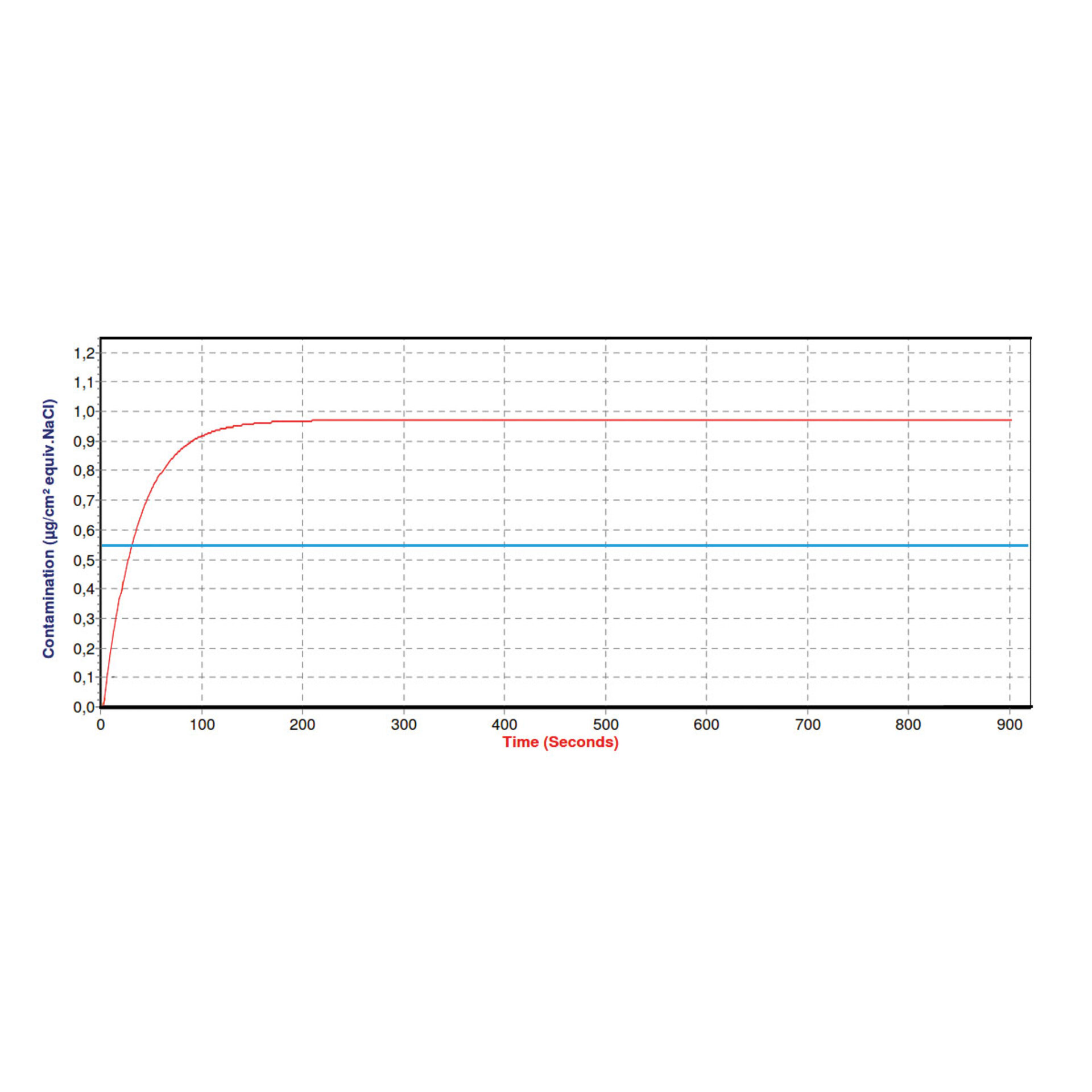
Ionic Conatmination Measurement (ROSE Test)
-
Extractive, quantitative detection of total ionic contamination in the range of 0.01 - 30 μg/cm2
-
According to IPC-TM-650 2.3.25
-
Comparison of cleanliness levels and/or production monitoring as a supplement to Technical Cleanliness
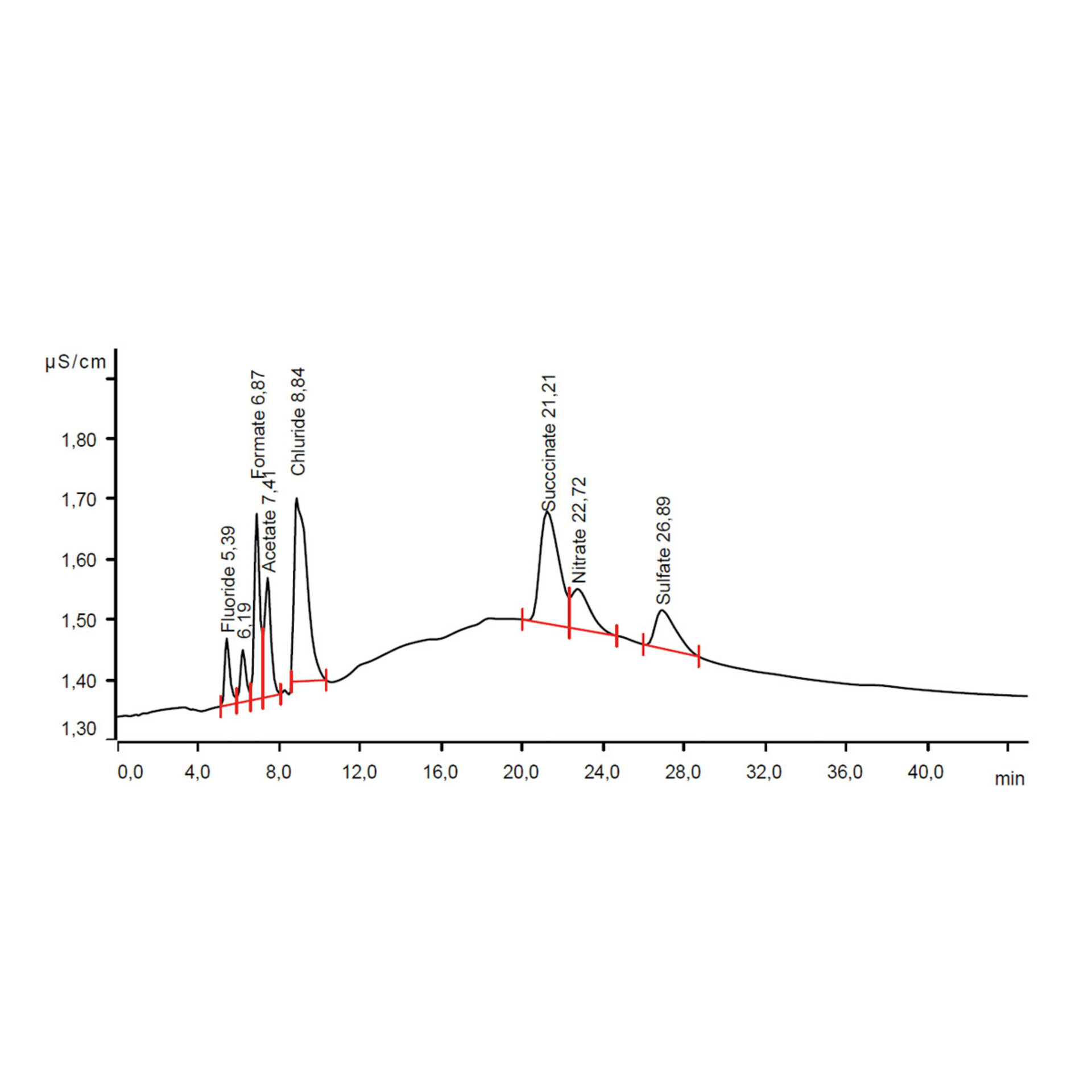
High-resolution analysis Ion Chromatography
The measurement using ion chromatography is also based on the electrical conductivity of ions and is governed by IPC-TM-650 2.3.28.
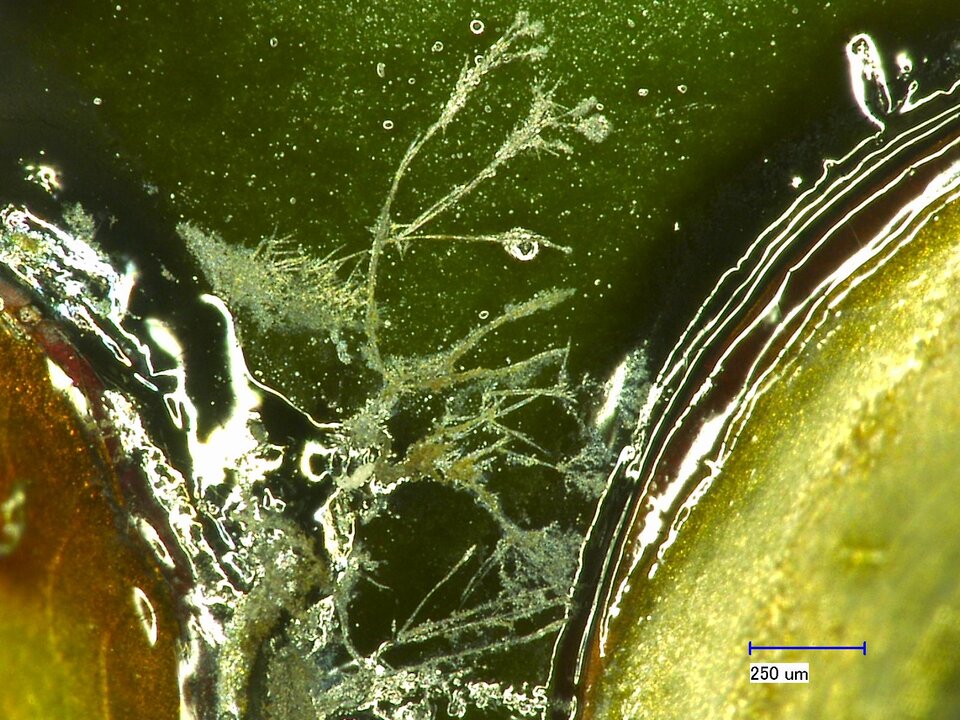
While the ROSE Test provides only a summation value of ionic contamination, ion chromatography allows for high-resolution analysis of ions through specialized separation columns. It enables the determination not only of ion quantities but also of specific ion species responsible for contamination in electronics. This allows cleaning processes to be optimized selectively, effectively avoiding damages caused by ionic contamination.
Ion Chromatography (IC)
-
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of anions and cations (especially activators)
-
Detection limit: 0.01 μg/cm2
-
Comparison with requirements from standards
-
Evaluation of contamination's influence on the cause of damage
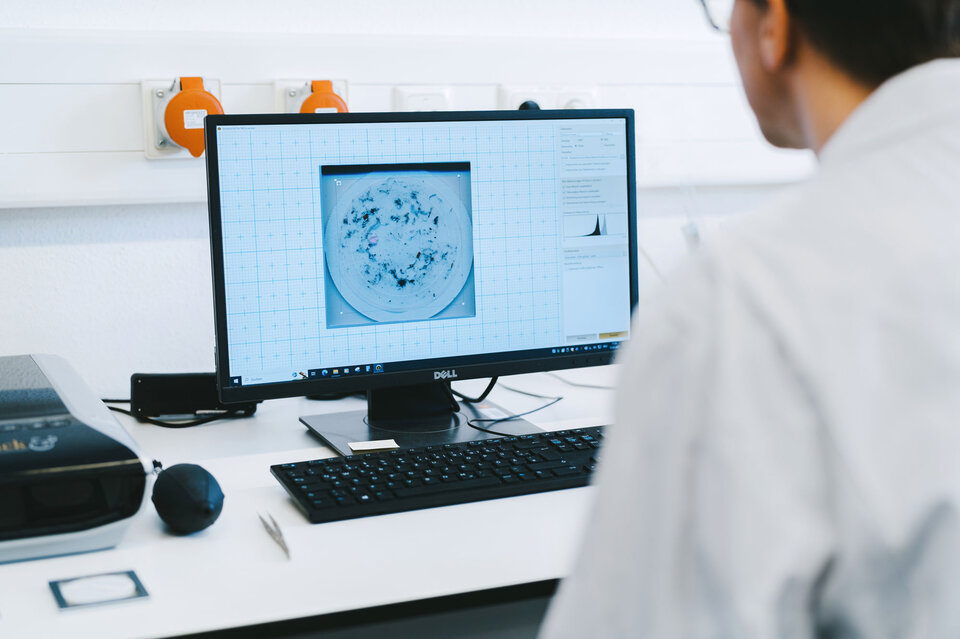
ion chromatography (IC) - what you can expectPrecise Breakdown of Contamination
Ion chromatography enables precise analysis of ionic contamination on circuit boards and assemblies. This method provides the following information:
-
The type of ions responsible for the contamination
-
The exact quantity of each ion
-
The quality of the contamination composition
-
An estimation of the origin and hazard potential of the contamination
For example, the presence of salts of weak organic acids on flux residues on the assembly can indicate specific causalities. Such conclusions can potentially be made for many ions relevant to electronic manufacturing.
The correct interpretation of found ions and knowledge of their interactions can allow for detailed inferences about the origin of the contamination.
Our application engineering experts can answer how this may affect your manufacturing, processing, or cleaning processes and suggest appropriate remedies.
Assistance ModuleIonic Contamination - ROSE Test & Ion Chromatography
Ionic contamination threatens the reliability of electronic assemblies. In this module, you will learn how ROSE testing and ion chromatography are used for measurement and evaluation. You will gain practical insights and concrete approaches to ensure the long-term ionic quality of your products.


whitepaper-collectionIonic Contamination
Avoid malfunctions and errors in electronic components caused by ionic contamination. Take appropriate measures to prevent and control this risk.
Read our whitepapers on "Ionic Contamination" now to deepen your expertise.