InsightsThe Underestimated Danger: How Moisture Affects Electronic Assemblies
Moisture can cause significant issues, so a good understanding of the risks and appropriate protective measures is crucial.
Moisture on electronic assembliesEffects of Moisture on Electronic Assemblies
The diverse consequences of moisture on electronic assemblies should not be underestimated. From short-term disruptions to long-lasting and severe damage, moisture can cause significant issues for the performance and lifespan of electronic components. Therefore, developing a comprehensive understanding of potential risks is crucial to taking appropriate protective measures.
varied causes How Moisture Enters Electronic Assemblies
Moisture can infiltrate electronic assemblies in various ways, with environmental conditions and temperature fluctuations playing a significant role. Assemblies can absorb moisture from their surroundings, especially when operated or stored in humid or highly fluctuating climate conditions. High humidity, fog, or condensation are factors that can lead to moisture reaching the surfaces of the assemblies.
During the manufacturing process, moisture and water vapor can be trapped. Improper handling of assemblies during assembly or repair can introduce fingerprints, sweat, or other contaminants onto the assembly, which can also attract moisture. Even during soldering processes, rapid temperature changes can lead to condensation on the surfaces of the assemblies, especially when the assemblies are transferred from a cooler environment to the soldering area.
Furthermore, inadequate seals or enclosures can allow moisture to penetrate the assembly. This can be caused by aging, damage, or poor quality of the seals.
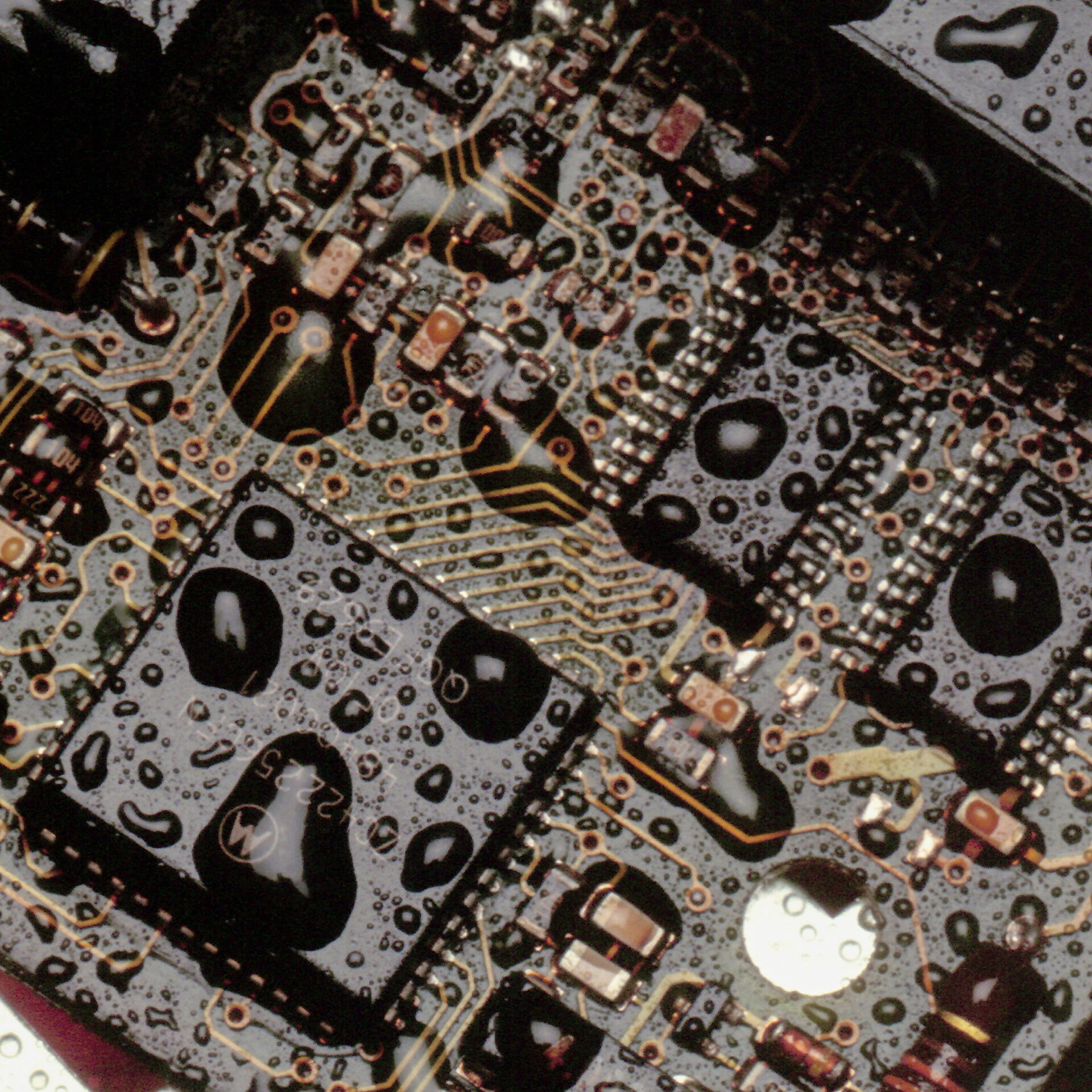
failure mechanismsFailure Mechanisms Due to Moisture Influence
Moisture on an electronic assembly can cause a variety of failure modes, including:
![]() Conductivity and Short Circuits
Conductivity and Short Circuits
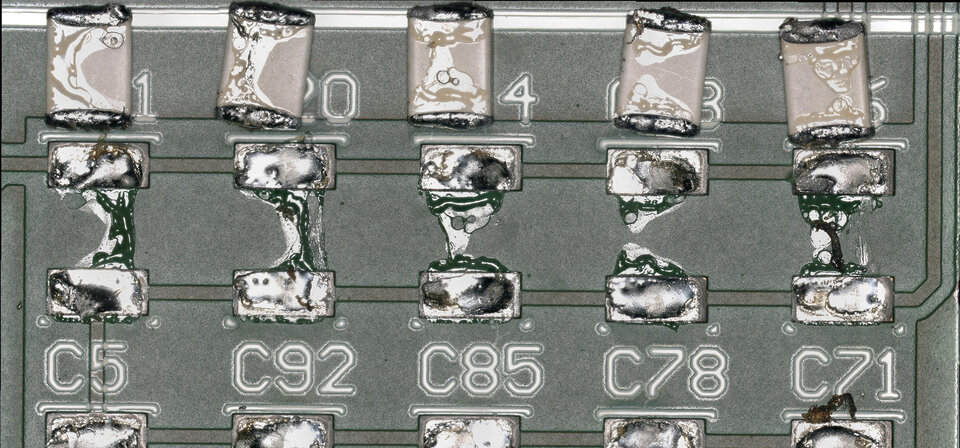
The situation becomes critical when moisture contains conductive contaminants or when contaminants dissolved by moisture reach the assemblies. This promotes the formation of connections between traces and components. Such short circuits can lead to the destruction of the assembly and, depending on its function, potentially pose dangerous consequences for people.
![]() Oxidation and Corrosion / Electrochemical Migration
Oxidation and Corrosion / Electrochemical Migration
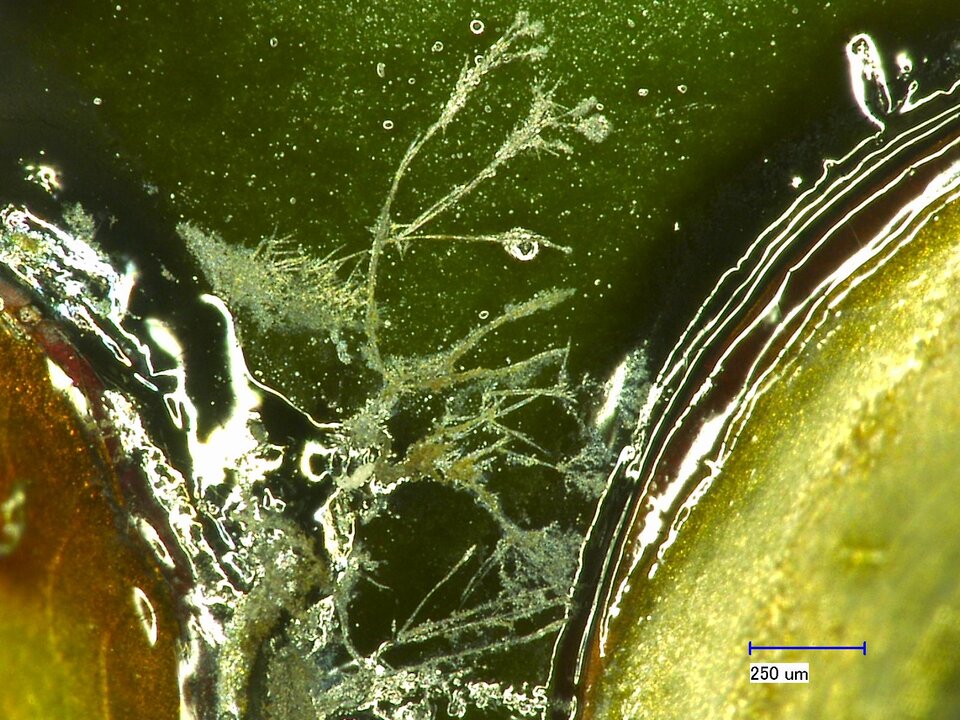
Moisture can promote the oxidation of metal contacts and connections on the assembly, leading to a deterioration of electrical conductivity. Electrochemical migration, a form of corrosion, also affects the reliability and lifespan of electronic assemblies and is often responsible for climate-related failures
![]() Dielectric Constant
Dielectric Constant
Moisture can increase the dielectric constant of insulation materials, affecting the electrical functionality of the assembly by increasing capacitance and causing signal distortion.
![]() Thermal Properties
Thermal Properties
The penetration of moisture can also affect the thermal conductivity of materials, hindering the effective heat dissipation of components. This, in turn, can lead to excessive heat buildup and premature failure
risk MinimizationEffective Protection Against Moisture in Electronic Assemblies
To minimize the effects of moisture on electronic assemblies, preventive measures are essential. These include:
-
Use of suitable enclosures and seals
-
Control of humidity in production and storage areas
-
Use of moisture-resistant materials
-
Implementation of protective coatings on the assembly
Mitigating moisture with coatingsWhat Can Be Achieved with Protective Coatings?
Protective coatings serve to shield the surfaces of assemblies from moisture, chemicals, dust, and other environmental factors. They form an insulating layer and act as a physical barrier between assembly components and the environment.
For a quick and reliable assessment of your protective coating, we offer various test methods such as the ZESTRON Coating Layer Test, Coating Reliability Test, and Iodine Vapor Test. Our experienced team is ready to assist with the execution and evaluation of these tests.
In case of (field) failures in your assemblies, our experts are prepared to identify the root cause and find solutions.
Whitepaper-collectionMoisture and Material-Induced Failure Mechanisms in Power Electronics
The whitepaper discusses the impact of moisture on the reliability of power modules in renewable energy systems and electric vehicles. It explores how moisture can alter the typical failure mechanism from electrochemical migration (ECM) to anodic-cathodic migration (AMP) and provides specific case examples.
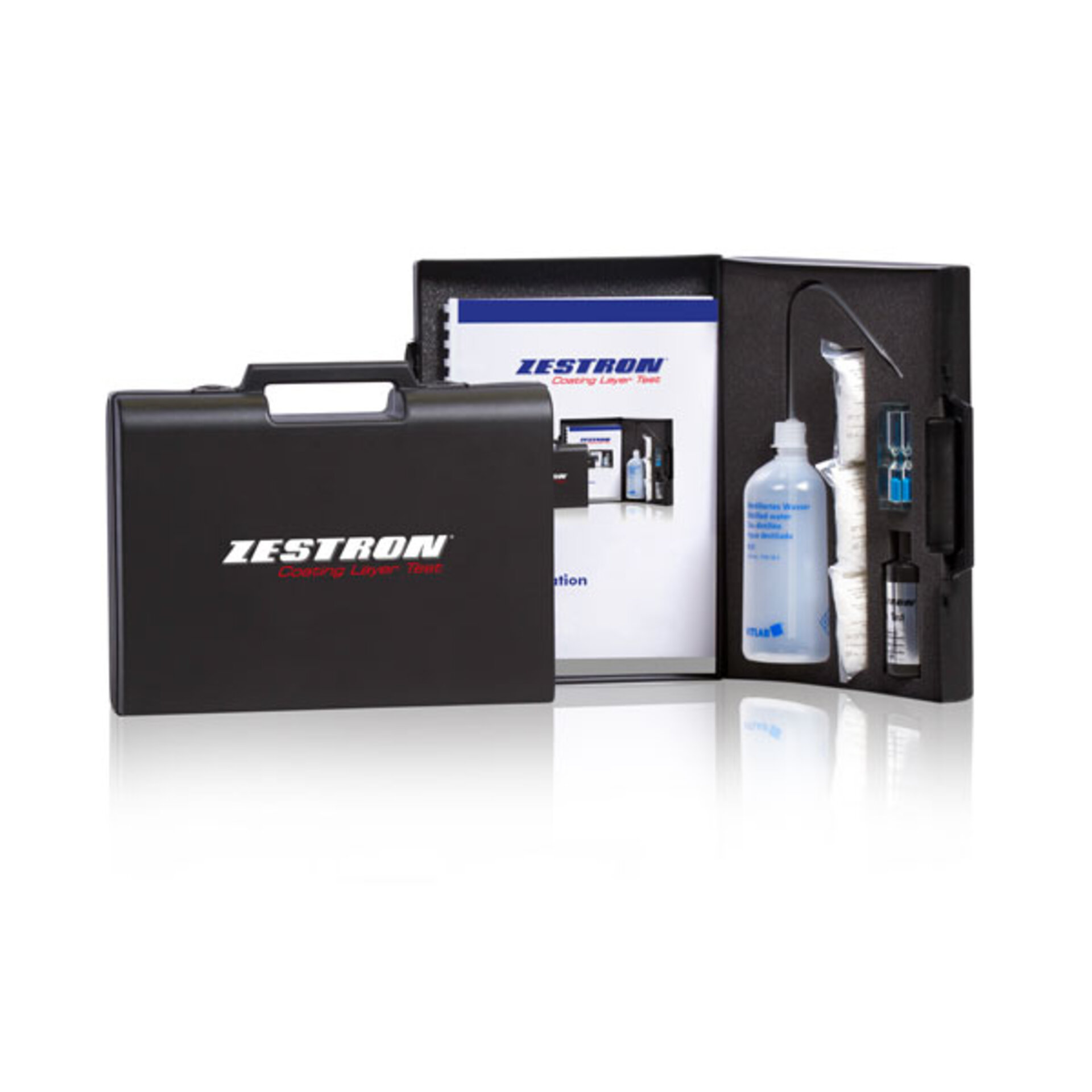


product recommendationCoating Layer Test
The ZESTRON Coating Layer Test visualizes coating defects on electronic assemblies and verifies component wetting before soldering.