Humidity Robustness for PCBAs and Power Electronics
Classify moisture-related failures reliably, substantiate root causes, and implement corrective actions through effectiveness verification.
Humidity robustness Why Moisture-Related Failures Are Rarely a Coincidence
Moisture becomes a failure driver when several factors act simultaneously: conductive moisture films, electric field strengths, ionic residues, particles, critical geometries as well as material composites and protective systems. This combination leads to leakage currents, drift, corrosion or short-circuit events, often initially sporadic and difficult to reproduce.
If moisture-related failures occur or humidity risk needs to be mitigated, a structured assessment is the next step.
Request a consultation
Confidential and structured. With NDA on request.
Typical faults & failure mechanismsWhat Typically Happens in Moisture-Related Failures
Moisture failures often do not manifest themselves as an immediate total failure, but as intermittent faults that occur under certain climatic and load conditions and disappear again during normal operation.
Typical problems in the field:
-
Faults occur depending on the weather, storage or transportation conditions
-
Anomalies intensify under climatic conditions and electrical load
-
Symptoms range from functional drift to dropouts or short-circuit events
-
Visible indications are possible (deposits, traces of corrosion, dendritic structures, particles), but not necessarily present
Examples of possible causes of failure and failure mechanisms
Moisture-related failures can cause very different types of damage. Correct classification is crucial because the boundary conditions and failure paths differ significantly depending on the cause.
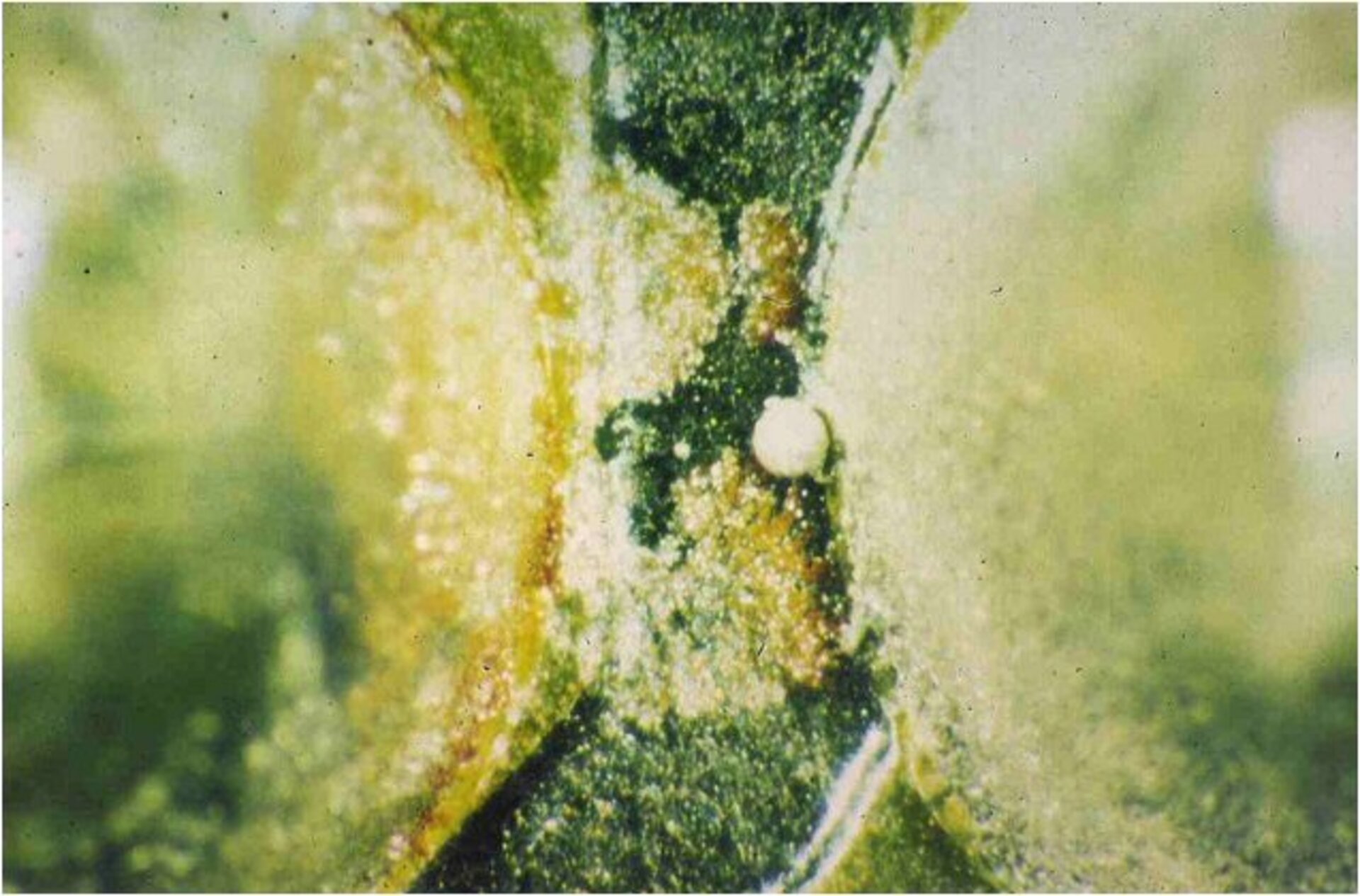
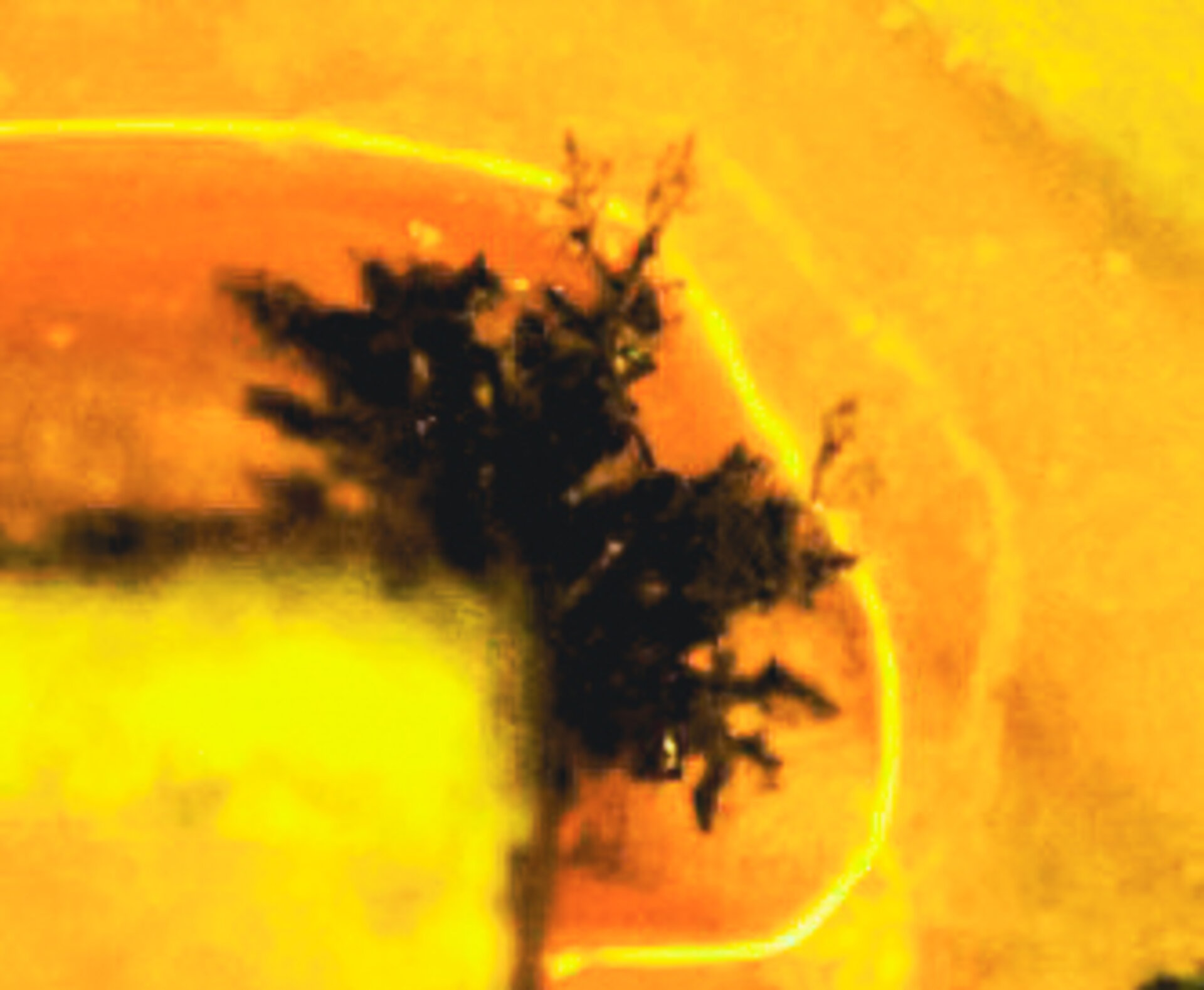
1 | Electrochemical Migration (ECM)
Dendrites can form conductive bridges on the PBA surface and trigger short circuits, especially in the event of condensation.
Typical failure: intermittent short circuit or sharp drop in insulation resistance when exposed to moisture.

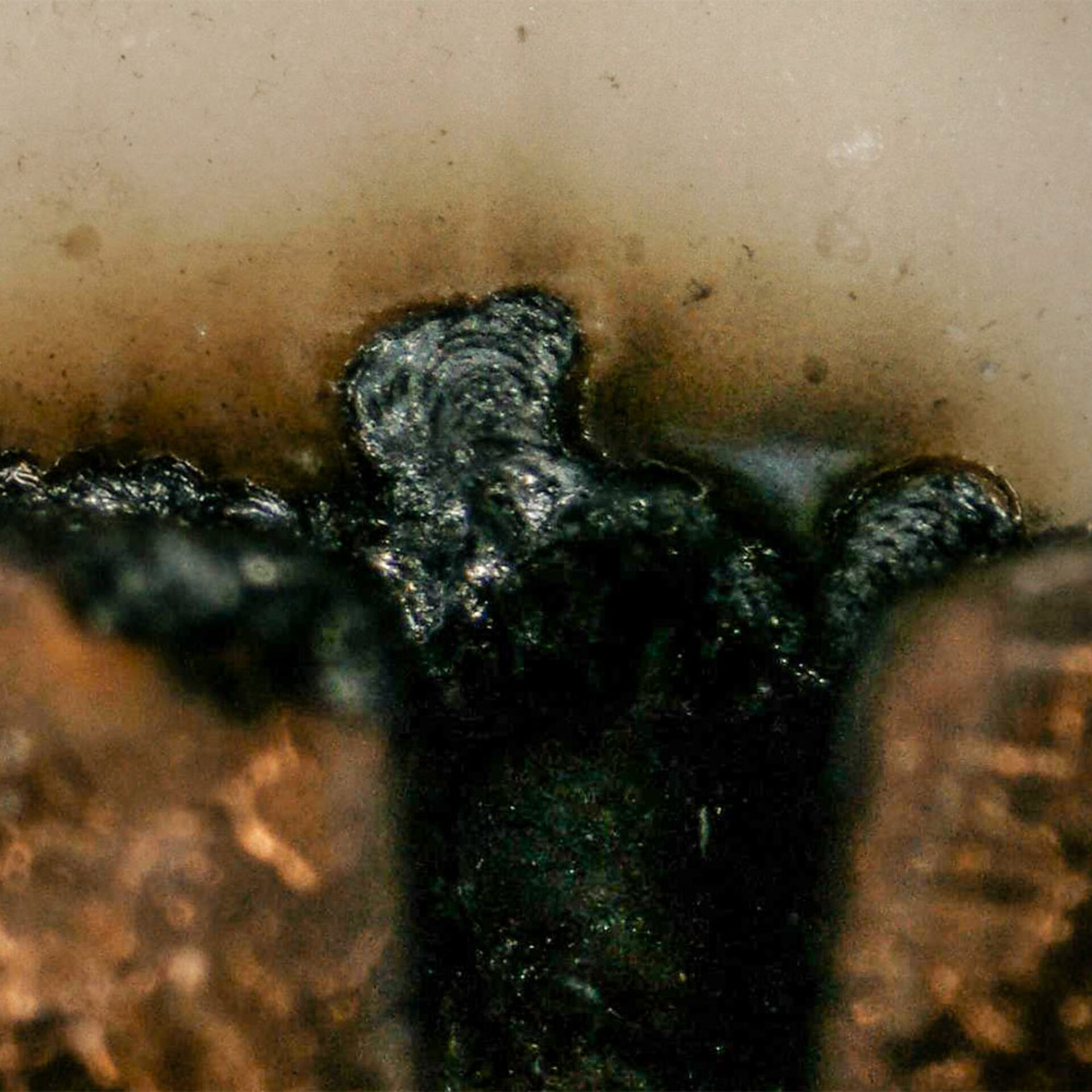
2 | Anodic Migration Phenomenon (AMP)
Conductive paths between layers as a result of Electrochemical Migration, favored by a weakened layer bond.
Typical failure: breakdown or increase in leakage current in the laminate.

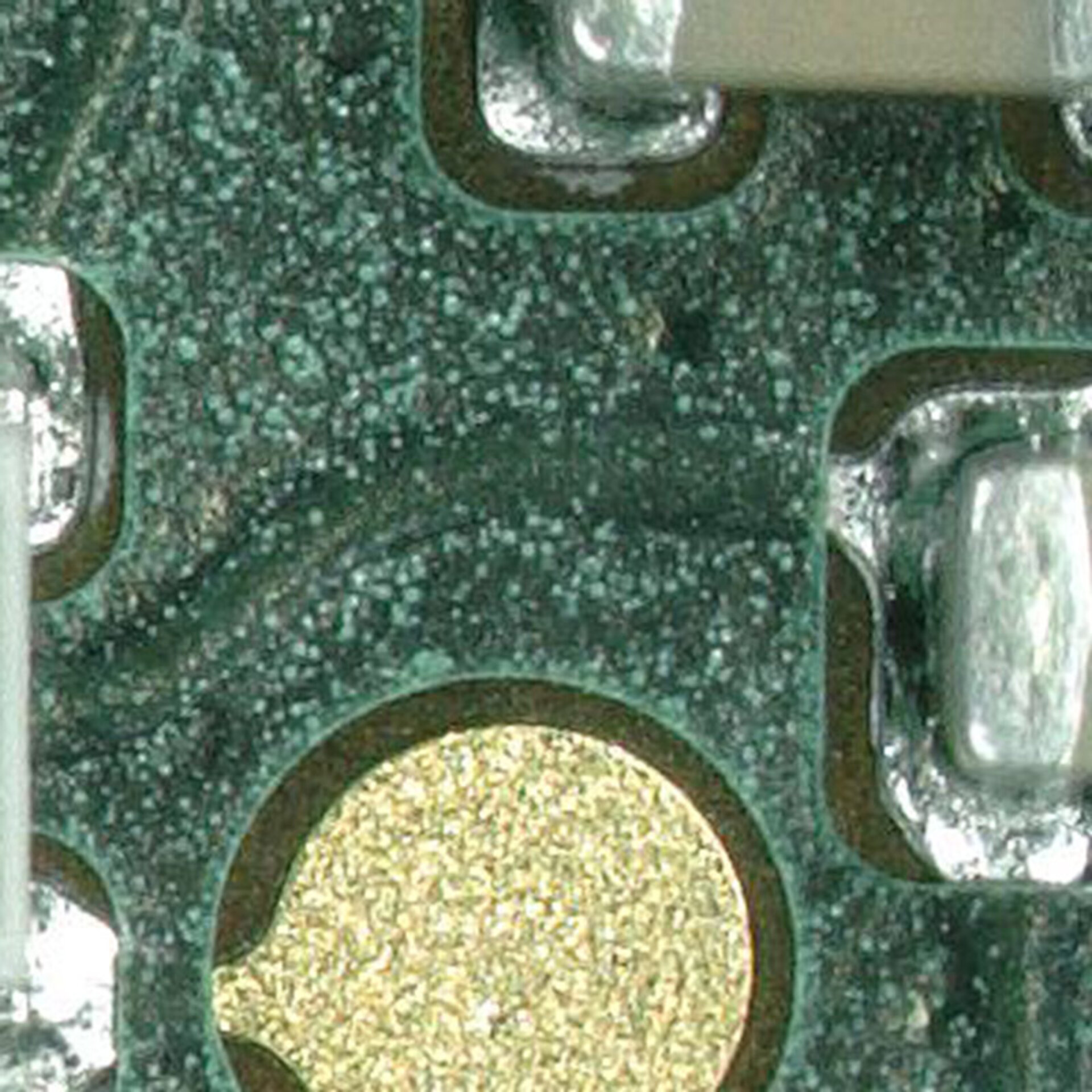
3 | Water Treeing
Combination of AMP-like degradation in the layer composite and local discharges in micro-gaps and pores under moisture stress.
Typical failure: gradual deterioration of the insulation with increasing leakage currents.

4 | Insertion Loss
Moisture or particles can influence the insulation resistance at switching frequencies typically from 100 kHz and attenuate the signal transmission.
Typical failure: Functional drift or conspicuous changes in the signal parameters without a classic short circuit.
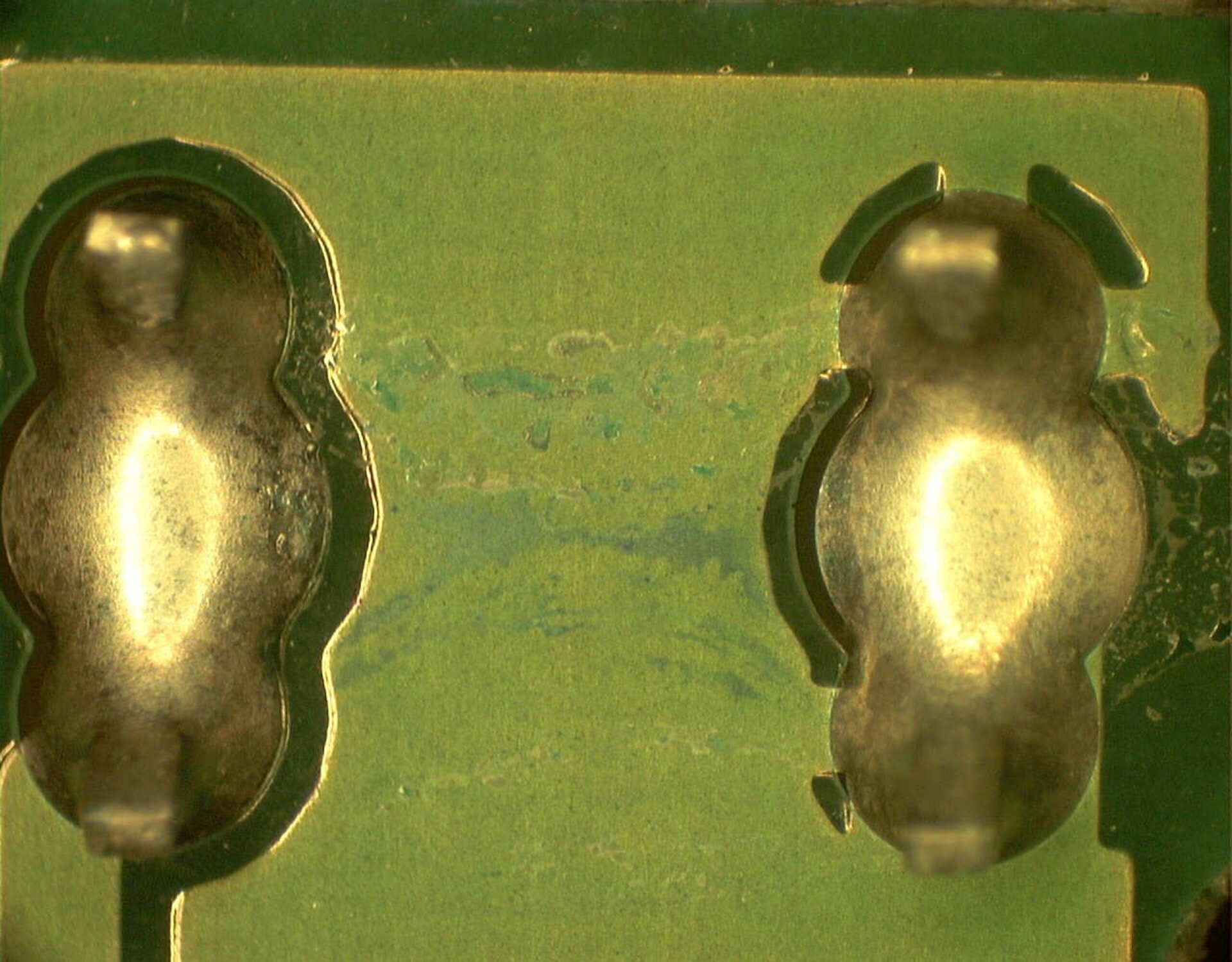
5 | Parasitic Leakage Current
Moisture on and in polymeric protection systems can favor conductive paths, especially at temperatures typically above 120°C.
Typical failure: Increase in leakage current up to protective shutdown or sporadic malfunctions.
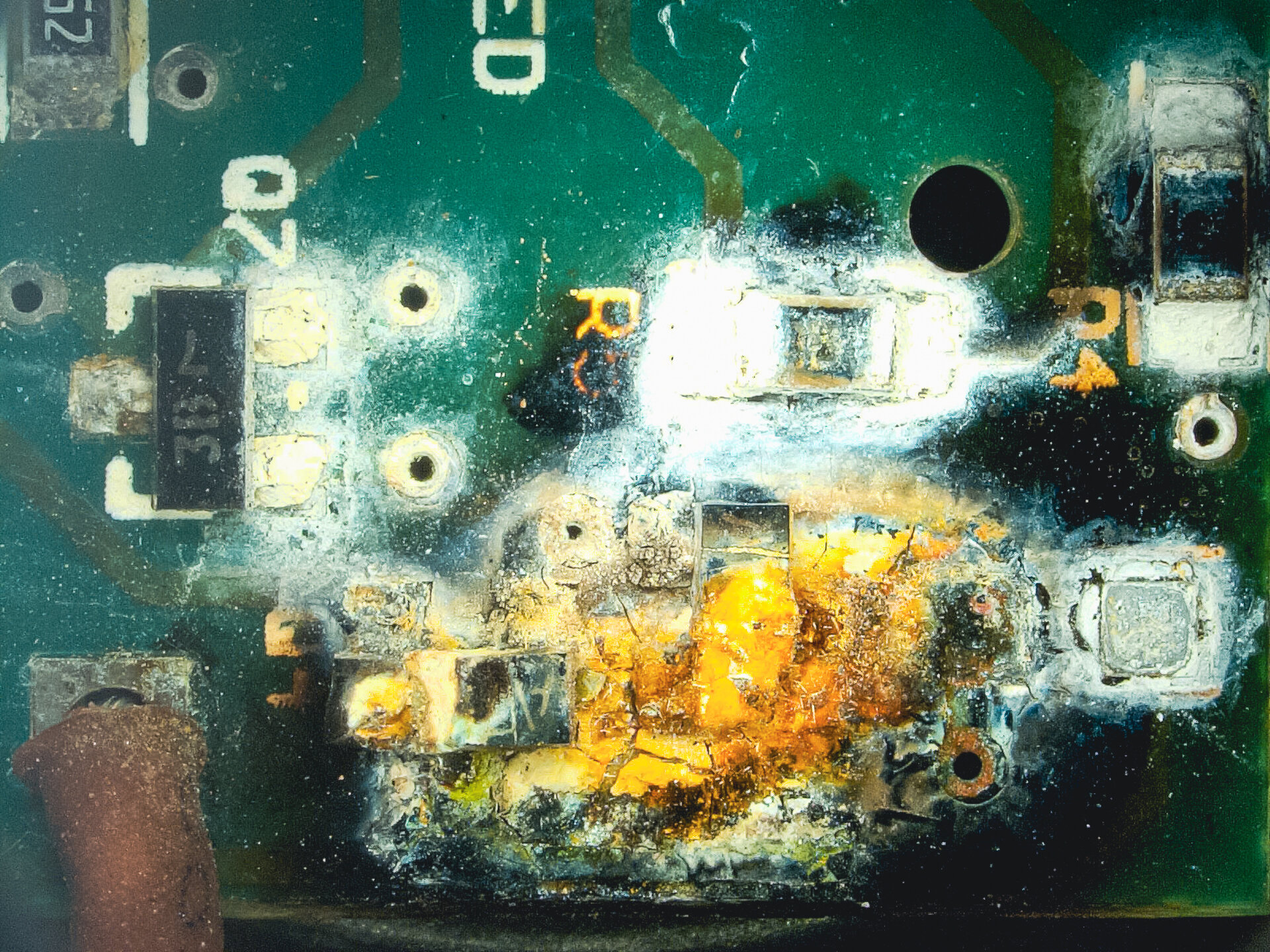

6 | Thermal Event
Conductive particles can trigger short circuits and cause consequential thermal damage.
Typical failure: abrupt short-circuit event with localized melting or fire.
From classification to reliable root cause analysis
On the basis of over 2000 processed cases, we create a comprehensible risk, damage and root cause analysis. The aim is a reliable classification that brings together the boundary conditions, failure paths and risk drivers in the system context.
Our support: your measurable benefitHow we provide support for moisture failures and moisture risks
Moisture-related failures are often addressed too late in day-to-day operations, because they are difficult to reproduce and diagnose. We provide targeted support at the process points where causes are narrowed down, risks are assessed and decisions are made for testing, design, process and protection concepts.
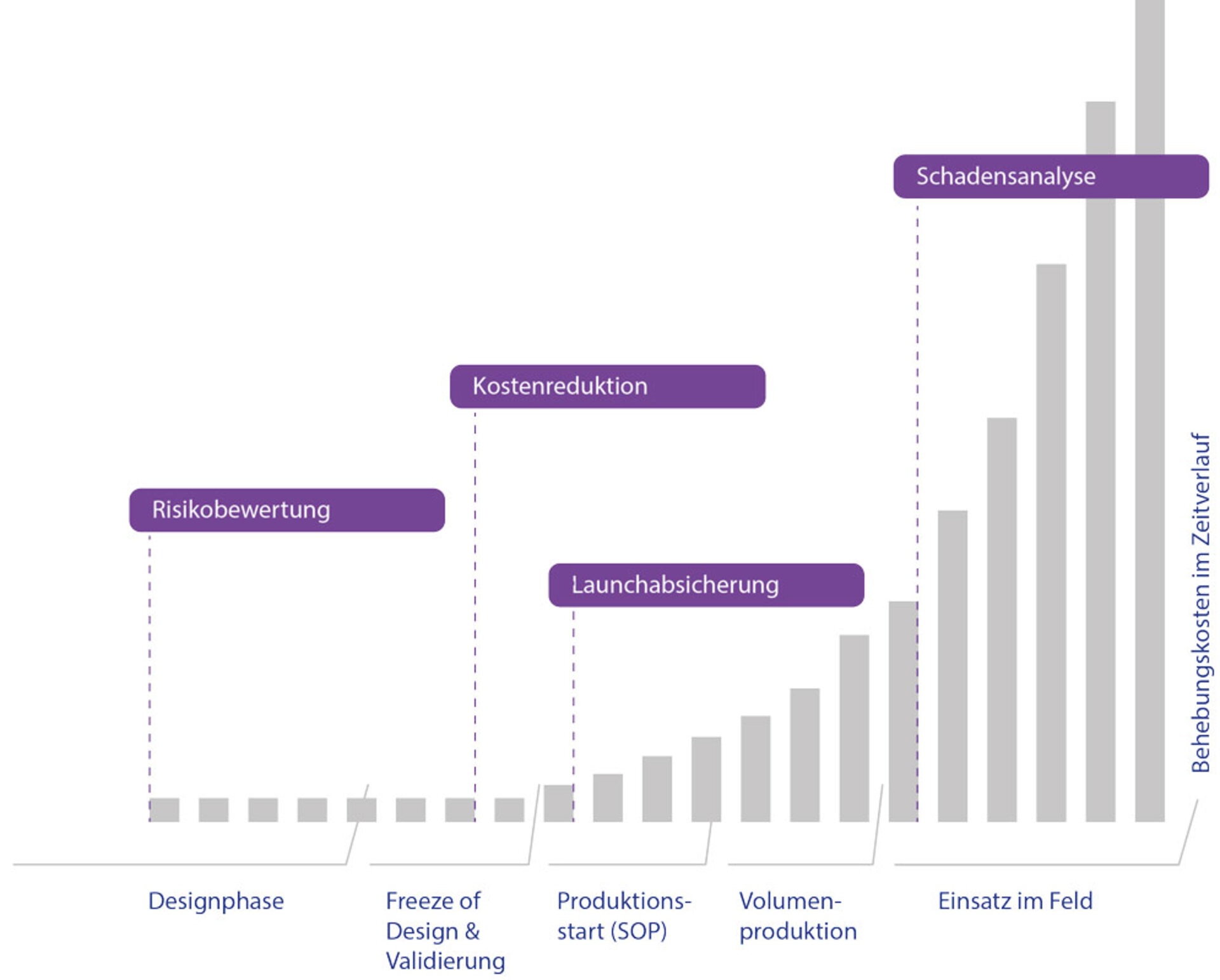
An overview of your benefits
-
Risk assessment: Identify and prioritize weak points in the structure, process and protection system, supplemented by suitable detection methods.
-
Cost reduction: Use reliability tests and process data to reduce unnecessary test scopes, rework and procurement costs.
-
Launch validation: Define and validate proof of specification and robustness for the start of series production.
-
Failure analysis: Classify failure patterns and causes in a comprehensible manner, derive measures and avoid consequential risks.
Early identification of weak points and targeted process optimization measurably reduce rework, rejects and complaint costs.
Contact usProfit from our analysis and implementation expertise
We deliver comprehensible, economically feasible recommendations for action in the system context. The collaboration is structured and confidential; if desired, also secured by a non-disclosure agreement (NDA).
Our experts work closely with your team, from the classification of individual issues to comprehensive risk, damage and cause analysis or system discussions, tailored to your needs.
ServicesSupport as required
Depending on the initial situation, we provide support with suitable formats from the initial classification to implementation in the production environment.


