PCB Cleaning: How Do You Produce Rinse Water of the Best Possible and Consistent Quality?
time for a fact checkEfficient Assembly Cleaning: Producing Rinse Water
On the Test Bench: How Is the Best Possible and Consistent Quality Ensured?
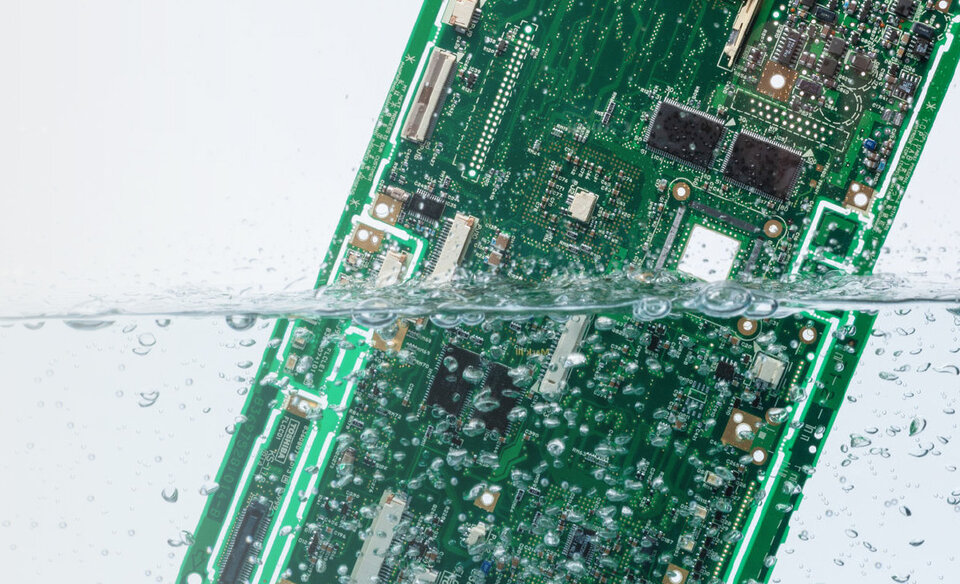
The cleaning process for electronic assemblies consists of three stages: cleaning, rinsing and drying. Each stage makes a significant contribution to the cleaning result and should be optimised. An optimally set rinsing stage ensures that previously dissolved impurities, such as flux, particles or residues of the cleaner, are removed from the surface of the assembly and do not leave any residues

In order to fulfil this function perfectly, rinsing water of consistently good quality is required, which must first be produced before it can be used in the cleaning process. But how is rinse water produced, recycled and easily monitored? Find out in this fact check.
Watch the Fact Check in the Video ▼
fact check to readPCB Cleaning: Production & Treatment of Rinse Water
On the Test Bench: What Materials Are Needed for Good Rinse Water Quality?
Why Is Rinsing So Important in the Cleaning Process?
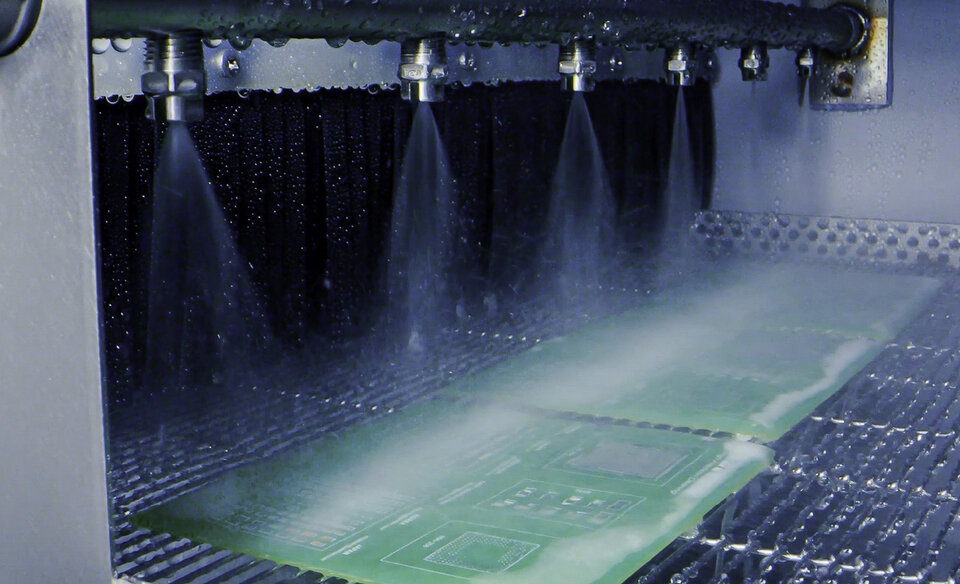
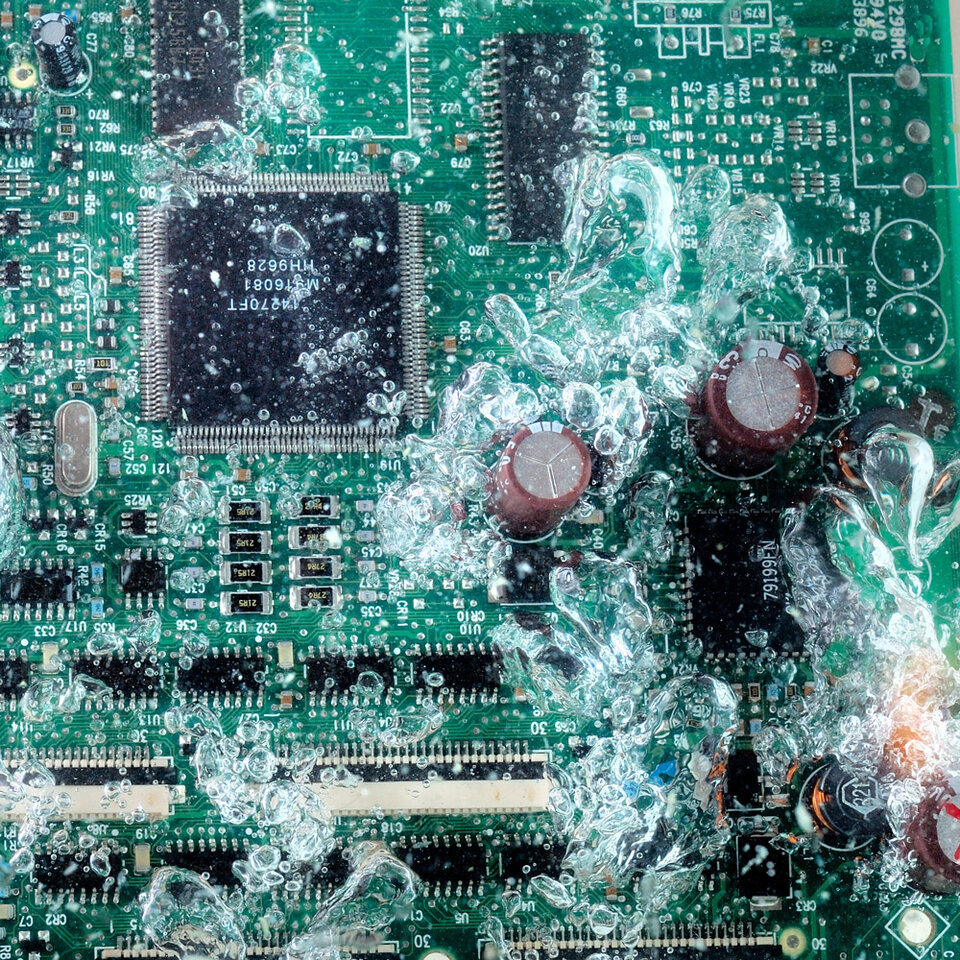
In the rinsing stage, residues of impurities and cleaning agents are rinsed from assemblies. The assemblies first undergo a coarse rinse and then a fine rinse. If the water used in the two rinsing stages does not fulfil the necessary quality criteria, there is a risk that residues will remain on the surface of the assembly and dry out. This can form the basis for failure mechanisms.
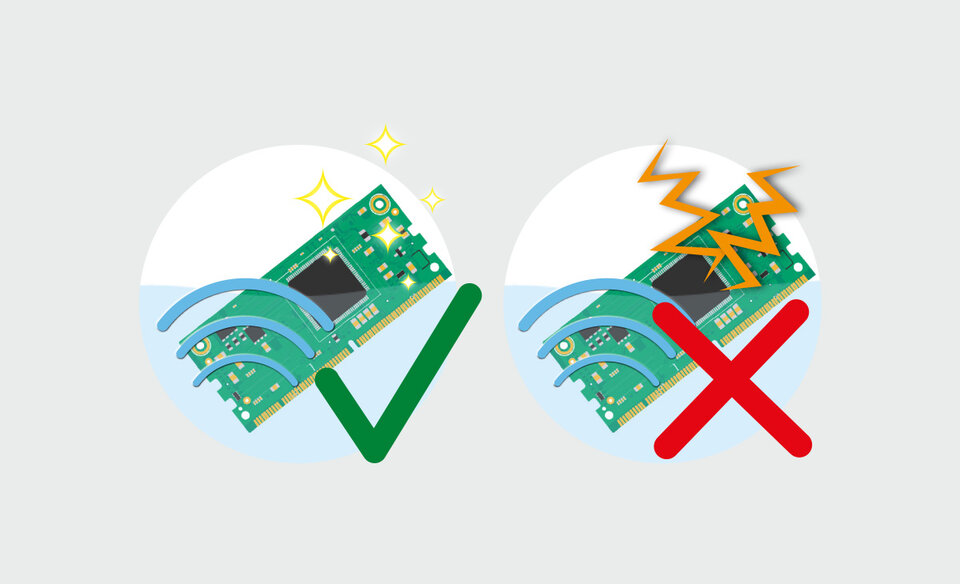
For example, ionic residues can lead to electrochemical migration or particles to bridging. Film-organic contaminants can impair the adhesion of coatings. In the worst case, these effects can lead to malfunctions and failures of assemblies.



The rinsing stage therefore makes an important contribution to an optimum cleaning result and the reliability of an electronic assembly. The rinsing water is crucial for this.
Why Does Rinse Water Need to Be Specially Treated and How Does This Work?
To fulfil its function, the rinsing water must meet certain quality criteria. For example, normal tap water is not suitable for rinsing the assemblies as it contains ions that lead to failure mechanisms. Instead, fully demineralised water is required, from which all anions and cations have been removed.
Particularly in cleaning systems with a closed-loop water management system, the quality of the rinse water depends not only on its production but also on its treatment. In this closed loop, used rinse water is recycled and waste water is avoided. A closed-loop system is usually found in systems for small to medium production throughputs.
You can get an overview of the various recirculation systems in the cleaning process in the Rinsing water fact check: What Needs to Be Considered in Water Management and Quality Monitoring?
The following auxiliary materials are required for demineralised water production and treatment:
-
Activated Carbon
-
Mixed Bed Resin
-
and Solid Filters



Carbon and resin ar supplied in ready made cartridges by specialised companies. However, the various auxiliary materials differ - both in price and performance.
In addition to the materials used for generation or treatment, monitoring the quality of the rinse water is also important. Monitoring water quality not only ensures consistent cleaning results but also indicates when activated carbon, mixed bed resin, and filters are exhausted and need to be replaced.
Fact Check on Rinse Water Treatment
Rinsing water - a complex and important topic in component cleaning
That's why we did a fact check and tested the performance of various activated carbons and mixed bed resins. We also answer the following questions:
-
What impurities are present in the rinse water, where do they come from and why do they need to be removed?
-
What simple measurement methods are used in practice?
-
What function do filters, activated carbon and mixed bed resin fulfil in rinse water treatment?
-
How often do they need to be replaced and can you do it yourself?
-
And what else should be considered whith activated carbon, mixed bed resin and filters?